The Fusion of Art and Science in the Enlightenment
The Fusion of Art and Science in the Enlightenment painting came as thinkers and artists searched to explore the natural world through reason and observation. 7
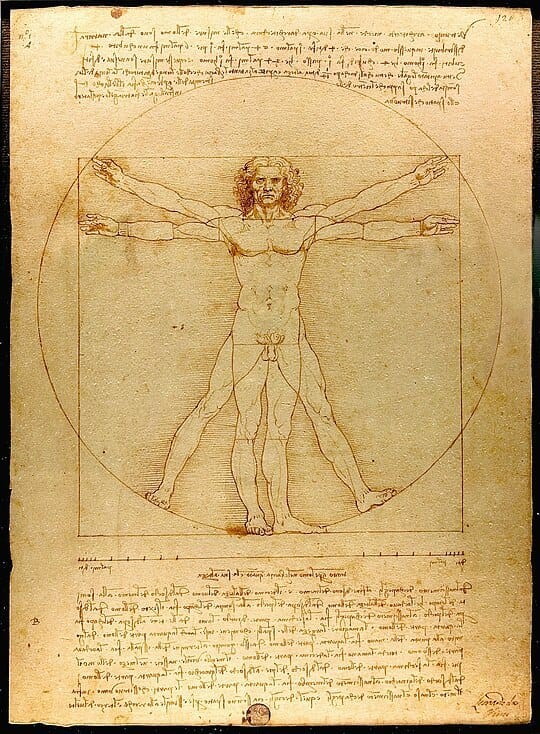
Artists like Leonardo da Vinci illustrated this fusion, using scientific principles in their work. The period highlighted rationality and empirical evidence, influencing fields like anatomy, perspective, and botanical illustration, leading to an improvement. Where art conveyed scientific ideas and science inspired artistic expression.
This collaboration fostered advancements in highlighting the interconnectedness of human knowledge. This fusion, influenced by shared values and mutual influence, resulted in a rich combination of artistic works that reflected the scientific discoveries and philosophical ideas of the time.
By discovering the intersection of art and science in Enlightenment paintings, we can gain a greater understanding of the intellectual and cultural landscape of this transformative era.
What was enlightenment and why does it matter today?
The Enlightenment was an intellectual movement that flowed across Europe during the 17th and 18th centuries. Characterised by a profound belief in reason, progress, and human potential, it marked a significant shift in how people thought about the world, society, and government.
The enlightenment had a profound impact on Western civilization. It inspired revolutions in France and the United States, set the stage for modern democracy, and encouraged progress in science, technology, and the arts.
Why does the Enlightenment matter today?
The Enlightenment was a pivotal period in human history that laid the foundation for many of the values and institutions that shape our world today. Its legacy continues to inspire and inform our efforts to create a more equitable, and prosperous society.
How does art and science begin to intertwine?
The intertwining of art and science during the Enlightenment was a product of shared values, mutual influence, collaborative efforts, and a shared interest in the natural world. This convergence led to significant advancements in both fields and laid the foundation for the continued relationship between art and science in subsequent centuries.
Understanding the Enlightenment: A Movement of Reason and Innovation
The Role of Scientific Thought in Enlightenment Culture
Scientific thought played a central role in Enlightenment culture. The Scientific Revolution, which preceded the Enlightenment, had established the foundation for a new approach to understanding the natural world. Scientists like Galileo Galilei, Isaac Newton, and Johannes Kepler made innovative discoveries that challenged traditional beliefs and established the foundations of modern science.
Enlightenment thinkers accepted the scientific method and applied it to various fields, including philosophy, politics, and economics. They pursued to discover the laws governing human society and the natural world through empirical observation and rational inquiry. This emphasis on scientific thought led to significant advancements in fields such as astronomy, medicine, and engineering.
Art as a Reflection of Scientific Advancement
Enlightenment art often reflected the scientific advancements of the era. Artists often use scientific techniques and principles in their work. The use of perspective, developed during the Renaissance, was refined and perfected during the Enlightenment, allowing artists to create more realistic and immersive compositions.
The study of optics and colour theory influenced artists’ understanding of light and colour, leading to new and innovative artistic styles.
The Influence of Science on Artistic Themes and Subjects
Rationalism in Portraits and Landscapes: Order and Precision
The Enlightenment’s focus on reason and logic influenced artistic themes and subjects, particularly in the realms of portraiture and landscape painting. Portraits often depicted individuals in a rational and objective manner, focusing on their intellectual qualities and contributions to society.
The use of geometric shapes, symmetrical compositions, and precise details reflected the Enlightenment’s order recognition and precision. Landscape paintings often depicted natural scenes in a rational and systematic way, emphasising the harmony and order of the universe. Artists used perspective to create a sense of depth and to represent the world accurately. The inclusion of scientific instruments, such as telescopes or microscopes, in landscapes focuses more on the connection between art and science.
Depicting Scientific Discoveries: Astronomy, Anatomy, and Beyond
Enlightenment artists were fascinated by scientific discoveries and often combined them into their work. Astronomy, in particular, was a popular subject, with artists depicting celestial bodies, constellations, and astronomical phenomena.
The Invention of the telescope allowed for more accurate observations of the cosmos, inspiring artists to create increasingly realistic and detailed depictions of the heavens. Anatomy was another important subject for Enlightenment artists. Advances in medical knowledge and the study of the human body led to more accurate and detailed depictions of the human form.
Artists studied anatomical drawings and dissections to better understand the structure and function of the human body, resulting in more realistic and expressive portraits and figures. Beyond astronomy and anatomy, Enlightenment artists also studied other scientific subjects, such as botany, zoology, and geology.
They created detailed illustrations of plants, animals, and geological formations, contributing to the scientific understanding of the natural world.
Humanism and Nature: Balancing Beauty with Scientific Observation
While the Enlightenment focused reason and logic, it also celebrated humanism and the beauty of the natural world. Artists often sought to balance scientific observation with artistic expression, creating works that were both informative and aesthetically pleasing.
Landscape paintings, in particular, often combined scientific accuracy with artistic beauty. Artists depicted natural scenes in a realistic manner, but they also sought to capture the emotional and spiritual qualities of nature.
The use of colour, light, and composition could convey a sense of awe, wonder, and reverence for the natural world.
Portraits could be both scientifically accurate and emotionally evocative. Artists sought to capture not only the physical features of their subjects but also their inner qualities and personalities.
By combining scientific observation with artistic expression, Enlightenment artists created works that were both informative and inspiring.
Key Artists and Their Contributions to Enlightenment Art
Joseph Wright of Derby: Illuminating the Age of Science
Joseph Wright of Derby (1734-1797) was an English painter known for his dramatic and innovative depictions of scientific experiments and industrial scenes. His work captured the excitement and wonder of the Enlightenment era, showcasing the power of human reason and technology.
Enlightenment paintings of joseph Wright
He’s most famous two paintings are:
I. A Philosopher Lecturing on a Terrestrial Globe, Before a Group of Listeners(1766): This iconic painting shows a group of people gathered around a globe, listening to a philosopher’s lecture.
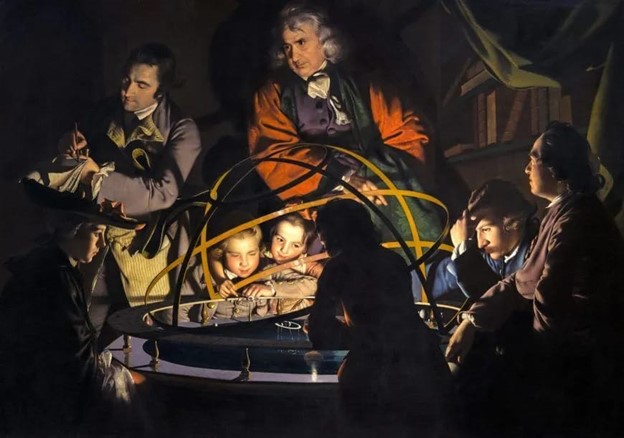

The dramatic lighting and the focused expressions of the audience express the intellectual curiosity and excitement of the Enlightenment.
II. Experiment on a Bird in an Air Pump (1768): This painting shows a scientific experiment in which a bird is placed inside a glass chamber and the air is gradually removed.

The contrasting emotions of the observers, including a fascination to horror, reflect the complex relationship between scientific inquiry and human emotion.
Jean-Baptiste-Simenon Chordin: Still Life and the Study of Nature
Jean-Baptiste-Simenon Chardin (1699-1779) was a French painter famous for his intimate and realistic still life’s. His work often focused on everyday objects, such as fruits, vegetables, and household items.
Chordin’s paintings were admired for their attention to detail, their subtle colour palettes, and their ability to capture the beauty and simplicity of ordinary life.
Enlightenment paintings of Jean-Baptiste-Simeon Cardin,
He’s most famous paintings are:
I. The Governess (1739): This painting shows a young girl and her governess participating in a quiet activity.

The peaceful atmosphere and the careful attention to detail create a sense of intimacy and calmness.
II. The Kitchen Maid (1760): This painting portrays a humble kitchen maid performing her daily tasks.
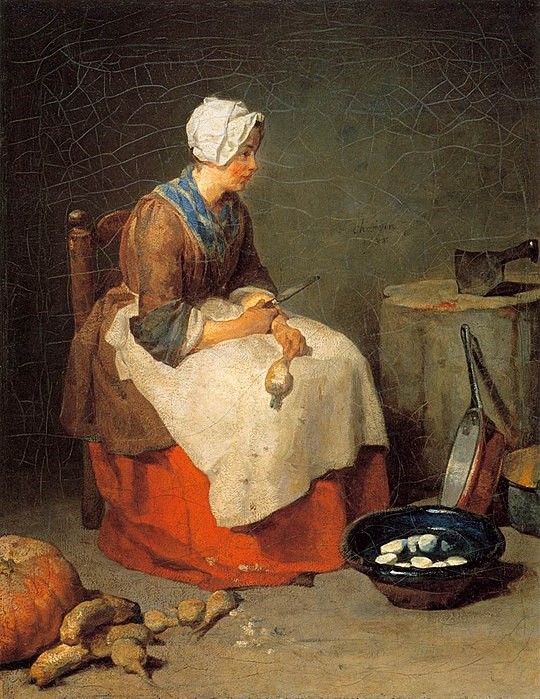

The realistic depiction of the figure and the objects in the scene reflects Chardin’s interest in the everyday life of ordinary people.
Jacques-Louis David: Art as a Symbol of Reason and Revolution
Jacques-Louis David (1748-1825) was a French painter who played a significant role in the development of Neoclassicism, an artistic style inspired by Greek and Roman art. His work often reflected the political and social ideals of the Enlightenment, particularly the emphasis on reason, order, and civic virtue.
Enlightenment paintings of Jacques-Louis David,
He’s famous paintings are:
I. The Oath of the Horatii (1784): This painting depicts a scene from Roman history, in which three brothers pledge to defend their country
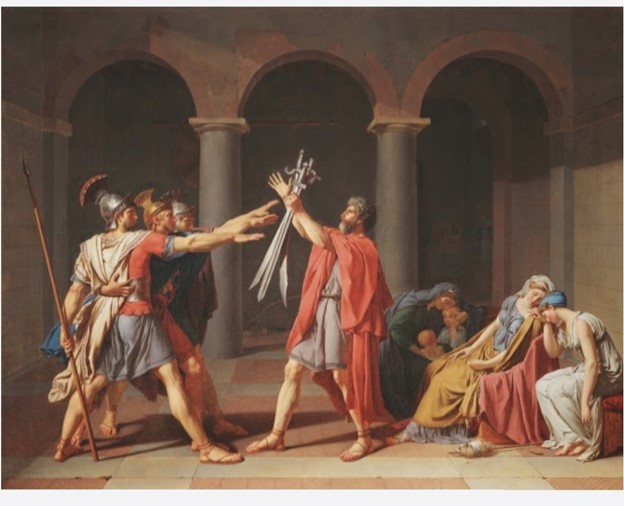

The strong, heroic figures and the dramatic composition reflect the ideals of patriotism and sacrifice that were central to the Enlightenment.
II. The Death of Marat (1793): This painting honours the assassination (murder) of Jean-Paul Marat, a radical journalist and politician during the French Revolution.
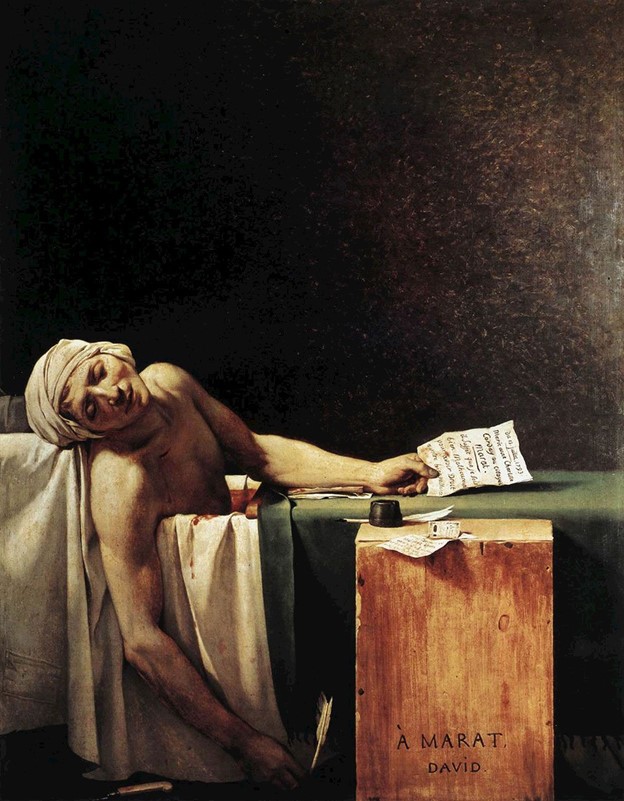

The stark simplicity of the composition and the dramatic portrayal of Marat’s death make it a powerful symbol of the Revolution and its ideals.
Scientific Advancements That Shaped Artistic Techniques
The Use of Optics and Linear Perspective in Painting:
The Enlightenment saw a significant advancement in the understanding of optics and Linear perspective, a mathematical system for representing three-dimensional space on a flat surface, was developed during the early modern era.
But it was more refined and popularised during the Enlightenment. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Andrea Mantegna experimented with perspective to create more realistic and immersive compositions.
Scientific theories of light also influenced artistic techniques. Artists began to study the properties of light, such as its intensity, colour, and direction. This understanding allowed them to create more accurate and dramatic lighting effects in their paintings.
For example, Rembrandt van Rijn was a master of chiaroscuro, a technique that uses strong contrasts between light and shadow to create dramatic effects.
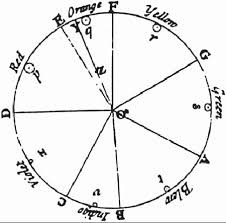
Colour Theory: The Influence of Newton’s Discoveries:
Isaac Newton’s discoveries about light were particularly influential on Enlightenment artists. In his book Optic’s, Newton described how white light is composed of a spectrum of colours. This discovery led to a new understanding of colour theory and its application in art.
Artists began to experiment with colour mixing and the effects of different colours on the viewer. Johannes Vermeer was a master of colour harmony, using complementary colours to create a sense of depth and richness in his paintings. William Hogarth explored the psychological effects of colour in his “Harlot’s Progress” series, using warm colours to represent vice and cool colours to represent virtue.
Scientific Advancements Reflected in Techniques:
Leonardo da Vinci’s Last Supper (1495) is a masterpiece of perspective and composition.
Rembrandt van Rijn’s The Night Watch (1642) is a dramatic example of chiaroscuro.
Johannes Vermeer’s Girl with a Pearl Earring (1665) is renowned for its use of colour harmony.
William Hogarth’s Harlot’s Progress series (1731-1732) demonstrates the use of colour to convey moral messages.
These examples explain how scientific advancements in optics and colour theory shaped the techniques and styles of Enlightenment artists, contributing to the development of more realistic and expressive works of art.
The Legacy of Enlightenment Paintings in Future Movements
From Enlightenment to Neoclassicism: Art as Precision and Idealism
The Enlightenment’s significance on reason, order, and precision influenced the Neoclassical movement that followed. Neoclassical artists drew inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman art, which was characterised by its clarity, simplicity, and idealism. The scientific precision of Enlightenment art, particularly in terms of perspective and anatomy, helped to inform Neoclassical artists’ pursuit of ideal forms and harmonious compositions.
Neoclassical architecture is a prime example of this influence. Buildings like the Pantheon in Paris and the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C., were designed to embody the ideals of reason, order, and civic virtue. The use of classical architectural elements, such as columns, arches, and domes, reflected the Neoclassical movement’s admiration for ancient Roman architecture.
The Emotional Response: How Enlightenment Art Paved the Way for Romanticism
While the Enlightenment emphasised reason and objectivity, it also laid the groundwork for the Romantic movement, which gives importance to emotion, imagination, and the individual experience.
The Enlightenment’s focus on scientific inquiry and the exploration of the natural world helped to create a sense of awe and wonder, which would later be accepted by Romantic artists.
Romantic artists often sought to express their emotions and feelings through their art. They were drawn to the sublime, the beautiful, and the mysterious aspects of nature.
The Enlightenment’s focus on individual experience and the power of the imagination provided a foundation for Romantic artists to explore their own emotions and to express themselves in new and innovative ways.
The legacy of Enlightenment paintings can be seen in the subsequent Neoclassical and Romantic movements.
The Enlightenment’s emphasis on reason, order, and scientific inquiry influenced the precision and idealism of Neoclassical art, while its exploration of the natural world and individual experience helped to pave the way for the emotional and imaginative response of Romantic artists.
The Modern Relevance of Art and Science Collaboration
Contemporary Examples of Art and Science Intersecting:
The Enlightenment’s art-science relationship continues to resonate in today’s world. Scientific illustrations remain essential for communicating complex ideas to a large audience. Digital art has appeared as a powerful tool for visualising scientific data and creating immersive experiences.
For example, medical imaging uses advanced visualisation techniques to help doctors diagnose diseases and plan treatments.
This historical intersection of art and science continues to inspire artists, scientists, and educators today.
Current examples of art and science collaboration:
Bio Art: Artists working with living organisms and biological materials, investigating the intersection of art and biology.
Data Visualization: Artists using data to create visually stunning and informative representations of complex information.
Interactive Installations: Artists creating immersive experiences that combine technology, art, and science to entertain viewers.
The STEAM Movement: Bridging Creativity with Scientific Inquiry
The STEAM movement (Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Mathematics) shows the combination of these disciplines to foster creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking.
The STEAM movement aims to equip students with the skills and knowledge needed to address complex challenges in the 21st century. The legacy of the Enlightenment’s art-science relationship serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of creativity, innovation, and the power of human ingenuity.
The Lasting Impact of Enlightenment Art on Modern Creativity
Summarising the Influence of Enlightenment Paintings on Art and Science Today
The empact of Enlightenment Paintings on Art and Science Today, The Enlightenment’s art-science relationship has left a lasting legacy that persist to shape our world.
Enlightenment paintings exemplified the power of merging art and science, showing how these two disciplines can complement and improve each other. By incorporating scientific discoveries in their works, Enlightenment artists created creative and thought-provoking pieces that reflected the intellectual and cultural spirit of the time.
Encouraging Exploration of Art and Science in Modern Contexts
The intersection of art and science remains a vital and dynamic field today. By showing the works of Enlightenment artists and contemporary practitioners, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the ways in which art and science continue to shape our understanding of the world.
To learn more about the intersection of art and science:
Visit museums and exhibitions that feature Enlightenment art and contemporary works that show the relationship between art and science.
Read books and articles on the history of art and science, as well as contemporary trends in these fields.
Attend workshops and lectures that tell the intersection of art and science.
By actively Observing with these assets, you can intensify your understanding of the rich and complex relationship between art and science and its persistent impact on our culture and society.

